Executive Summary
The U.S. senior living industry is experiencing significant transformation as three major forces reshape the market landscape. New tax laws have created mixed effects on senior affordability through new tax benefits for middle-income seniors while reducing government assistance for lower-income populations. Industry bankruptcies have surged to a two-year-high, with senior living representing over 40% of all healthcare bankruptcy filings in recent quarters. Meanwhile, home healthcare services are expanding rapidly, with the market projected to reach $644 billion by 2034 as 88% of seniors express a preference for aging in place.
Despite these challenges, demographic trends create substantial long-term opportunities for senior living operators.
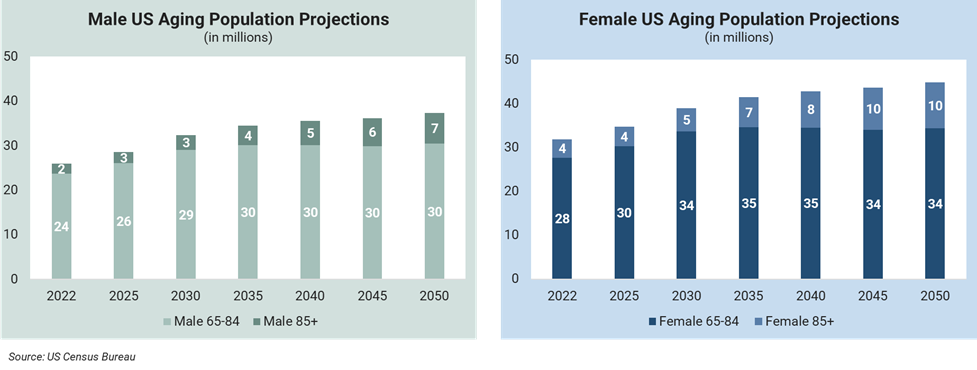
Senior living demand is projected to grow 35% over the next decade, driven primarily by approximately 60% growth in the over 85 population, assuming current penetration rates remain constant.
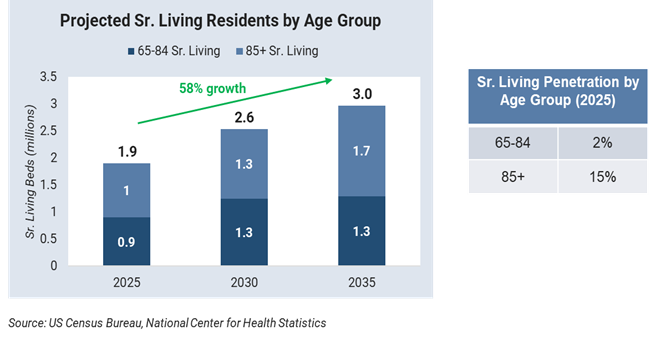
While this represents a significant opportunity, operators must navigate policy changes, financial pressures, and home health competition that could alter traditional demand.
Success in this transformed landscape demands strategic adaptation across multiple dimensions. Companies that effectively navigate policy changes, capitalize on consolidation opportunities from distressed competitors, and differentiate their services from home-based alternatives will strengthen their market position. Those that fail to adapt to these shifting dynamics risk falling behind in an increasingly competitive environment where operational excellence and strategic positioning have become essential for sustained success.
Policy Pressures: The OBBBA's Four-Pronged Impact On Senior Living
The One Big Beautiful Bill Act (OBBBA) — signed into law in July 2025 — creates both opportunities and challenges for senior living operators. While the legislation provides tax relief for many older Americans, it also introduces changes to healthcare coverage, government assistance programs, and eligibility requirements that affect resident affordability and facility operations. Understanding these policy changes is important for senior living operators planning for the evolving regulatory environment.
Tax Changes: Enhanced Affordability for Middle-Income Seniors
The legislation provides targeted tax relief for older adults, including a new $6,000 "bonus" deduction for taxpayers aged 65 and older with income of up to $75,000 ($150,000 for couples), increased State and Local Tax (SALT) deduction caps from $10,000 to $40,000, and permanent extension of reduced income tax rates. These benefits could offset federal taxes on Social Security for many middle-income seniors.
For senior living operators, these tax benefits may boost resident affordability and payment capacity. Middle-income seniors could see increased discretionary income, potentially supporting private-pay capacity and entrance fee financing. However, the temporary nature of key provisions (the senior deduction expires in 2029) creates planning uncertainty for both families and operators considering long-term care arrangements. The impact will vary significantly across care segments, with independent-living residents most likely to benefit from tax relief, while populations already relying on government assistance programs may see limited advantage from these income tax provisions.
ACA Marketplace Changes: Coverage Barriers for Pre-Medicare Seniors
The legislation affects the 5.5 million adults aged 55-64 who rely on Affordable Care Act (ACA) marketplace plans for health insurance. Enhanced premium tax credits that have kept marketplace coverage affordable are set to expire at the end of 2025, which will result in an estimated 75% average increase in out-of-pocket premium costs, while new documentation requirements add administrative barriers to enrollment. Though the immediate impact affects pre-Medicare adults, ACA marketplace instability signals broader healthcare coverage uncertainty that will likely shift more financial responsibility to private-pay arrangements.[1]
Senior living operators should expect continued ACA marketplace volatility to impact resident financial planning and payment capacity. Loss of comprehensive health coverage or increased healthcare costs may either delay facility entry due to financial constraints or accelerate transitions for those with chronic conditions requiring integrated healthcare services that senior living facilities can provide.
Medicaid Eligibility: Work Requirements Affect Coverage Access
New Medicaid work requirements mandate that recipients aged 19–64 work at least 80 hours per month or fulfill equivalent criteria to maintain coverage. An estimated nine-million Medicaid recipients between the ages of 50 and 64 face these requirements, creating coverage uncertainty for those nearing retirement or working part-time. Administrative complexity could result in eligible individuals losing coverage due to paperwork challenges.
For senior living facilities with mixed-pay models, these changes present significant planning challenges. The potential reduction in Medicaid-eligible residents could force facilities to adjust payor mix strategies, increasing dependence on private-pay residents. Operators may need to enhance private-pay marketing efforts and reconsider service offerings, while regional variation in state implementation requires localized strategic responses.
Food Assistance Changes: Indirect Impact on Housing Affordability
Changes to the Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP) create indirect pressure on senior housing affordability. Starting in October 2027, states must pay 5-15% of SNAP benefits (up from 0%) and could see administrative costs increase from 50% to 75%. To manage these new expenses, some states may restrict eligibility, limit benefits, or potentially withdraw from the program. With over 11 million people aged over 50 receiving SNAP benefits in 2023, these changes affect a substantial portion of the senior living target demographic.
Reduced food assistance affects seniors' discretionary income available for housing costs. For seniors considering the transition to senior living, decreased SNAP benefits mean less money available for entrance fees, monthly costs, or care upgrades. This could impact both the timing and level of care that prospective residents can afford, potentially pushing demand toward more basic service levels or delaying moves until financial pressure becomes acute.
Navigating the New Policy Landscape
The OBBBA creates a bifurcated market where middle-income seniors may benefit from tax relief while lower-income and pre-Medicare seniors face reduced government assistance and coverage barriers. Senior living operators must prepare for increased complexity in resident financial assessment, enhanced private-pay marketing strategies, and flexible service models that accommodate varying affordability levels. The temporary nature of many provisions and regional variation in state implementation require operators to develop market-specific strategies and scenario planning capabilities for both the implementation period and the eventual expiration of key benefits.
Financial Distress Is Accelerating Industry Consolidation
The senior living industry is experiencing an unprecedented wave of financial distress, with bankruptcy filings reaching a two-year-high in Q1 2025. Senior living now represents over 40% of all healthcare bankruptcy filings, marking the second consecutive quarter of leading healthcare bankruptcy activity.[2] This crisis reflects a convergence of operational challenges, debt maturity pressures, and margin compression that is fundamentally reshaping the competitive landscape.
Unprecedented Bankruptcy Wave
Senior living bankruptcies surged to seven filings in Q1 2025, more than doubling from three filings in Q4 2024, representing the highest quarterly total in two years. Major operators, including Pacifica Senior Living, filed Chapter 7 liquidation for 93 facilities with liabilities ranging from $10-50 million, while Petersen Health Care defaulted on over $50 million in loans despite generating $340 million in annual revenue. The scale of distress extends beyond individual operators, with some facilities reporting occupancy rates as low as 21%, as seen with Unisen Senior Living.
These bankruptcies create immediate market opportunities for well-capitalized operators and investors. Distressed asset acquisitions are becoming increasingly common, with facilities selling at significant discounts to replacement costs. However, the concentration of distressed properties also signals broader structural challenges that extend beyond individual operator performance, requiring sophisticated due diligence and turnaround expertise to navigate successfully.
Root Causes of Financial Distress
The current crisis stems from multiple converging factors, with debt structures proving particularly problematic as $2.2 trillion in commercial loans mature over the next three years. Many operators took on significant debt during the pre-pandemic expansion period, and current cash flows are insufficient to service these obligations amid ongoing operational challenges. Construction cost inflation has also created additional pressure, with mid-level assisted living facilities now costing $269-$361 per square foot, representing a 20-30% increase that affects both new development feasibility and existing facility valuations.[3]
Occupancy recovery remains incomplete across segments, with independent living still running 2.0 percentage points below pre-pandemic levels, while operators face margin compression of approximately 200 basis points due to elevated labor costs. The combination of reduced revenue from lower occupancy and increased operational expenses has created a cash flow squeeze that many operators cannot sustain without significant operational restructuring or capital injection.
Market Consolidation and Strategic Opportunities
The wave of financial distress is accelerating industry consolidation, as stronger operators gain market share through strategic acquisitions of distressed properties. Healthcare Real Estate Investment Trusts (REITs) achieved 24.2% returns in 2024, representing the best-performing real estate sector, indicating investor appetite for well-positioned senior living assets. However, regional banks are simultaneously limiting senior living exposure, creating a bifurcated capital market where access to financing depends heavily on operator strength and asset quality.
The current environment presents significant opportunities for operators with strong balance sheets and operational expertise. Distressed acquisitions allow for market share expansion at attractive valuations, while the reduced new construction pipeline (delivering only 5,000 units per quarter against a need for 775,000 additional units by 2030) supports long-term supply-demand fundamentals. Success in this environment requires sophisticated capital allocation, operational turnaround capabilities, and strategic market positioning.
Implications for Industry Strategy
The bankruptcy crisis highlights the critical importance of balance sheet strength and operational efficiency in the current market environment. Operators must focus on debt management, occupancy optimization, and cost structure alignment to avoid distress, while simultaneously positioning for growth opportunities created by competitor failures. The crisis also underscores the need for enhanced financial monitoring, scenario planning, and strategic flexibility to navigate an increasingly volatile operating environment where market leadership increasingly separates successful operators from those facing existential challenges.
Market Disruptions: The Home Health Revolution
The rapid expansion of home-based healthcare services represents a fundamental challenge to traditional senior living models, with the U.S. home healthcare market projected to reach $180 billion by 2030.[4] This growth is driven by strong consumer preference for aging in place — 88% of seniors prefer this option — and Medicare's strategic shift toward home-based care delivery.[5] However, aging in place presents significant challenges, particularly in rural areas where service delivery inefficiencies and limited provider networks create accessibility barriers. Urban seniors face different obstacles, including housing modifications for accessibility and higher costs for in-home services in dense metropolitan markets. The convergence of technology enablement, cost advantages, and changing family dynamics is creating compelling alternatives to facility-based care that senior living operators must address strategically.
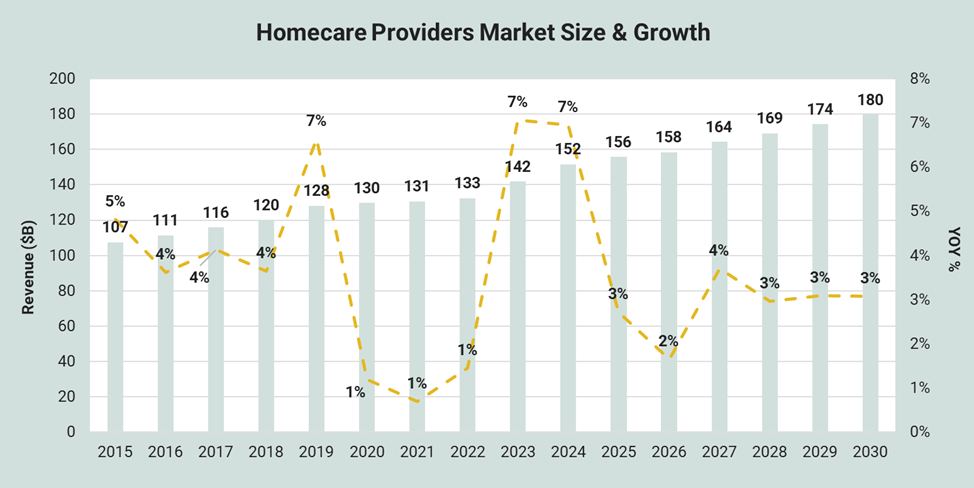
Source: IBISWorld report, Home Care Providers in the US, July 2025
Scale of Market Transformation
The home healthcare sector is experiencing explosive growth, with Medicare coverage expanding to shift up to $265 billion in services to home settings in 2025. Hospital-at-home programs now operate in over 350 hospitals across 37 states, demonstrating the mainstream acceptance of home-based acute care. Remote patient monitoring technology is advancing rapidly, enabling sophisticated care coordination that was previously only available in institutional settings.
This transformation directly impacts senior living occupancy and revenue models, with average length of stay declining across segments as families increasingly evaluate multiple care options throughout the aging process. The cost differential is significant, with home health aide services averaging $34 per hour compared to $5,900 monthly for assisted living, creating a compelling value proposition for cost-conscious families managing long-term care decisions.[6]
Competitive Dynamics and Business Model Disruption
Traditional senior living operators face unprecedented competition from unbundled service models that allow seniors to receive specific care components while remaining in their homes. Medicare Advantage plans increasingly incentivize home-based care options, aligning reimbursement structures with consumer preferences and cost management objectives. This shift challenges the fundamental value proposition of senior living communities, which have historically bundled housing, dining, social activities, and healthcare services into comprehensive monthly fees.
Major senior living operators are responding through strategic divestiture and repositioning. Brookdale Senior Living's $400 million sale of home health assets to HCA Healthcare signals industry recognition that competing directly with specialized home health providers may be less effective than focusing on core facility-based services. Some operators are developing hybrid models that combine facility and home-based services, while others are differentiating through specialized care programs and premium amenities that cannot be replicated in home settings.
Technology Integration and Service Innovation
The proliferation of AI-powered care platforms and remote monitoring devices is enabling sophisticated care coordination that bridges the gap between home and facility-based services. However, 77% of senior living operators identify interoperability as their top technology barrier, suggesting that many facilities lag home health providers in technology adoption and integration capabilities.[7] This technology gap creates both challenges and opportunities for senior living operators willing to invest in digital transformation.
Successful navigation of home health competition requires senior living operators to clearly articulate their unique value proposition beyond basic care delivery. This includes confronting loneliness through structured community engagement, which research shows improves longevity, along with security, comprehensive dining programs, and immediate access to higher levels of care as needs change. Operators must also consider strategic partnerships with home health providers rather than viewing them solely as competitors, potentially creating care continuums that serve seniors across multiple settings as their needs evolve.
Strategic Response to Market Disruption
The home health revolution requires senior living operators to fundamentally reconsider their market positioning and service delivery models. Success in this environment demands clear differentiation based on services that cannot be effectively delivered in home settings, enhanced technological capabilities to match consumer expectations, and flexible care models that can adapt to changing resident needs. Operators must also develop more sophisticated marketing strategies that address families' increasing consideration of home-based alternatives and demonstrate the specific advantages of community-based living for their target demographics.
Conclusion
The convergence of policy changes, financial distress, and market disruption requires senior living operators to fundamentally reassess their strategic positioning and operational models. The OBBBA creates a bifurcated market where middle-income seniors may benefit from tax relief while lower-income and pre-Medicare seniors face reduced government assistance and coverage barriers. Simultaneously, the unprecedented wave of bankruptcies and the rapid expansion of home health alternatives are reshaping competitive dynamics and forcing operators to adapt or risk obsolescence.
Immediate Strategic Priorities
Senior living operators must prioritize financial resilience through enhanced cash flow management and debt restructuring initiatives, while developing more sophisticated resident financial assessment capabilities to navigate policy-driven changes in payment capacity. Market consolidation creates immediate opportunities for well-capitalized operators to expand through strategic acquisitions of distressed properties, requiring sophisticated due diligence capabilities and operational turnaround expertise. Technology adoption has become critical for competitive positioning, particularly investments in integrated care platforms that differentiate senior living from home health alternatives while demonstrating clear value beyond basic care provision.
Long-Term Competitive Positioning
The home health revolution demands that senior living operators clearly articulate their unique value proposition through specialized care programs, social engagement opportunities, and comprehensive lifestyle amenities that cannot be replicated in home settings. This requires fundamental repositioning from healthcare-focused messaging to lifestyle and community-centered marketing that emphasizes the social, security, and convenience benefits of facility-based living. Regional variation in policy implementation requires market-specific strategies and scenario planning for both policy implementation periods and eventual benefit expirations, necessitating enhanced financial monitoring systems and adaptive service models.
The Path Forward
The senior living industry stands at a critical inflection point where traditional operating models face unprecedented challenges from multiple directions, but operators who successfully navigate this environment will emerge with stronger market positions and enhanced operational capabilities. Success requires immediate action on financial positioning, strategic investments in technology and operational capabilities, and sophisticated planning for an increasingly complex regulatory and competitive landscape. The organizations that thrive will view current disruptions as opportunities for strategic repositioning, demanding expertise in financial restructuring, operational optimization, and strategic planning that many operators may need to acquire through partnerships with specialized consulting firms.
Notes:
[1] https://www.americanprogress.org/article/older-adults-with-aca-coverage-would-face-steep-premium-hikes-under-house-republicans-one-big-beautiful-bill-act/
[2] https://seniorhousingnews.com/2025/07/17/inside-the-financial-human-impact-of-senior-livings-bankruptcy-trend/
[3] https://seniorhousingnews.com/2023/08/21/construction-labor-challenges-push-senior-living-project-costs-higher-in-2023/
[4] IBIS World
[5] https://www.healthyagingpoll.org/reports-more/report/older-adults-preparedness-age-place
[6] https://www.ultimatecareny.com/resources/how-much-does-home-care-cost-per-hour
[7] https://seniorhousingnews.com/2025/07/01/argentum-technology-survey-identifies-top-trends-barriers-in-senior-living/