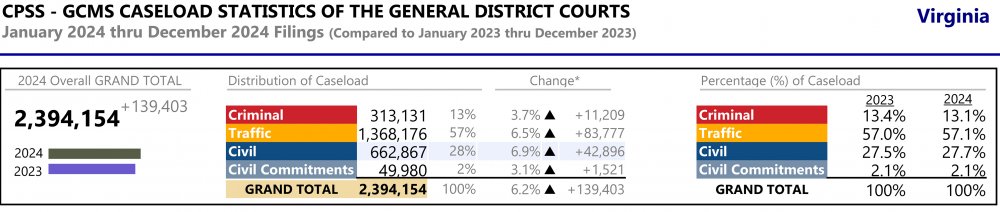
Civil lawsuit filings in Virginia's General District Courts increased more than 6% in 2024. The biggest increase? Warrants in debt (collection lawsuits) increased by 27%. A warrant in debt is a civil lawsuit to pursue recovery of money damages, usually due to unpaid debts and accounts receivable. Except for personal injury or wrongful death claims, Warrants in Debt are limited to a maximum recovery of $25,000. By contrast, unlawful detainer filings decreased by 8%. An unlawful detainer is an eviction lawsuit to pursue and obtain possession of real property (real estate) and unpaid rental charges, if applicable. There is no limit to the rental charges that can be pursued in an unlawful detainer filing.
Virginia’s Circuit Court civil filings increased modestly by 4% compared to 2023. Virginia Circuit Courts generally hear civil and commercial claims involving controversies of more than $25,000, along with family law, probate and estate claims, and real estate title claims, among other matters. Full data on 2024 legal filings from the Supreme Court of Virginia can be found here: 2024 Virginia General District Court filing data & 2024 Virginia Circuit Court filing data.
Landlords, tenants, property managers, lenders, creditors, and consumers in Virginia can take proactive steps to prevent costly litigation. Understanding your rights and obligations can minimize financial risks and avoid lawsuits related to unpaid debts or evictions.
Establish Clear Agreements
For landlords and creditors, well-drafted lease and loan agreements help prevent disputes. These should clearly define:
- Payment terms, due dates, and penalties for nonpayment.
- Responsibilities for property maintenance (landlords) and interest rates (creditors).
- Legal remedies in case of default.
Tenants and consumers should carefully review contracts before signing and seek clarification on any unclear terms.
Maintain Open Communication
Early communication can prevent minor issues from escalating. If you are a tenant, customer, or consumer behind on payments, consider:
- Informing landlords or creditors of financial difficulties.
- Requesting a payment plan, forbearance, or temporary extension.
- Keep records of all communications and agreements.
- Landlords and creditors should consider offering reasonable repayment options where feasible, as these are more efficient than litigation.
Follow Legal Collection and Eviction Procedures
Virginia law requires strict compliance with applicable eviction and collection procedures before pursuing eviction or debt collection lawsuits:
- Landlords must issue a proper notice of lease violation to tenants depending on the grounds sought for eviction.
- Creditors generally should send a formal demand letter before pursuing legal action.
Utilize Mediation and Alternative Solutions
Mediation can be a cost-effective way to resolve disputes without court involvement. Courts often encourage, but normally do not mandate, negotiations between parties to explore mutually beneficial solutions.
Understand the Legal Process and Consequences
If legal action becomes necessary:
- Landlords must file an Unlawful Detainer for eviction, attend a court hearing, and obtain a Writ of Eviction if a judgment is granted.
- Creditors must file a warrant in debt or other applicable lawsuits and obtain a court judgment before pursuing wage garnishment or other collection means.
- Tenants and consumers should respond promptly to court notices to avoid default judgments.
Seek Legal Guidance When Needed
Landlords, tenants, creditors, and debtors facing complex legal issues should consult an attorney to ensure compliance with Virginia law and protect their rights. By taking these proactive steps, all parties can reduce the risk of eviction and collection lawsuits, fostering more stable financial and housing relationships.